Legal Ways to Transfer Property to Family Members in India
Transferring property within the family can be done smoothly—if you choose the right legal route. Here are the most common methods:
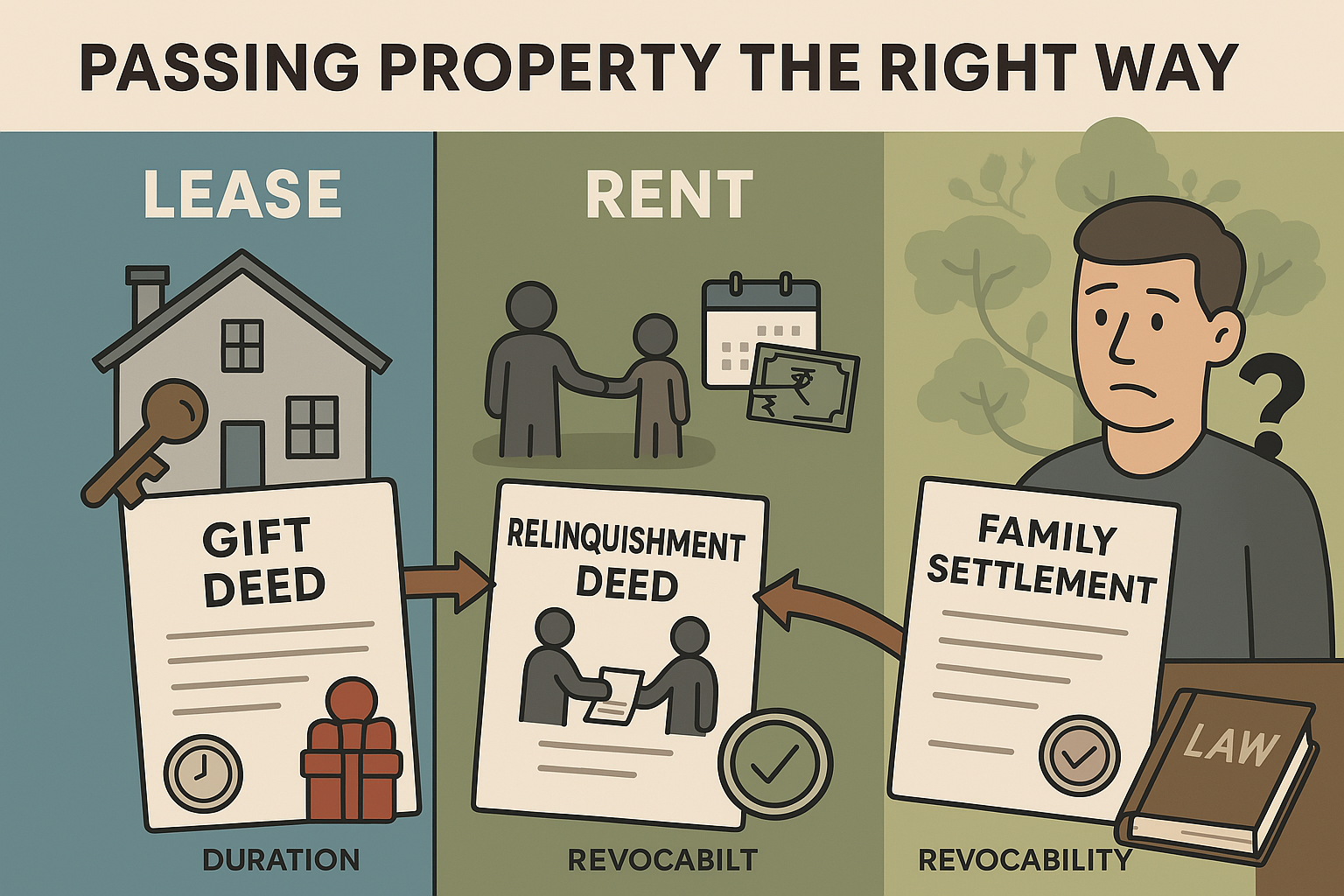
Gift Deed
-
Transfer without monetary exchange—done out of love and affection
-
Must be registered at the Sub-Registrar’s office
-
Stamp duty varies by state (often discounted for family transfers)
-
Irrevocable once registered
Relinquishment Deed
-
Used when a co-owner gives up their share to another co-owner
-
Common in inherited properties
-
Must be registered to be legally valid
-
No money involved unless specified
Will & Inheritance
-
Property passed on after death via a registered Will
-
If no Will, succession laws apply (Hindu Succession Act, Muslim Law, etc.)
-
Requires probate or succession certificate for legal transfer
-
No stamp duty on inheritance
Family Settlement Deed
-
Used to resolve disputes or divide property mutually
-
Avoids litigation and ensures clarity
-
Must be signed by all parties and registered
-
Stamp duty may apply depending on terms
- Lakshadweep
- Delhi
- Puducherry
- PROPIINN
- Arunchal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chhattisgarh
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Tripura
- Telangana | Andhra pradesh
- Pulse
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- West Bengal
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Chandigarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Ladakh