Hydropower Investments in Arunachal Pradesh
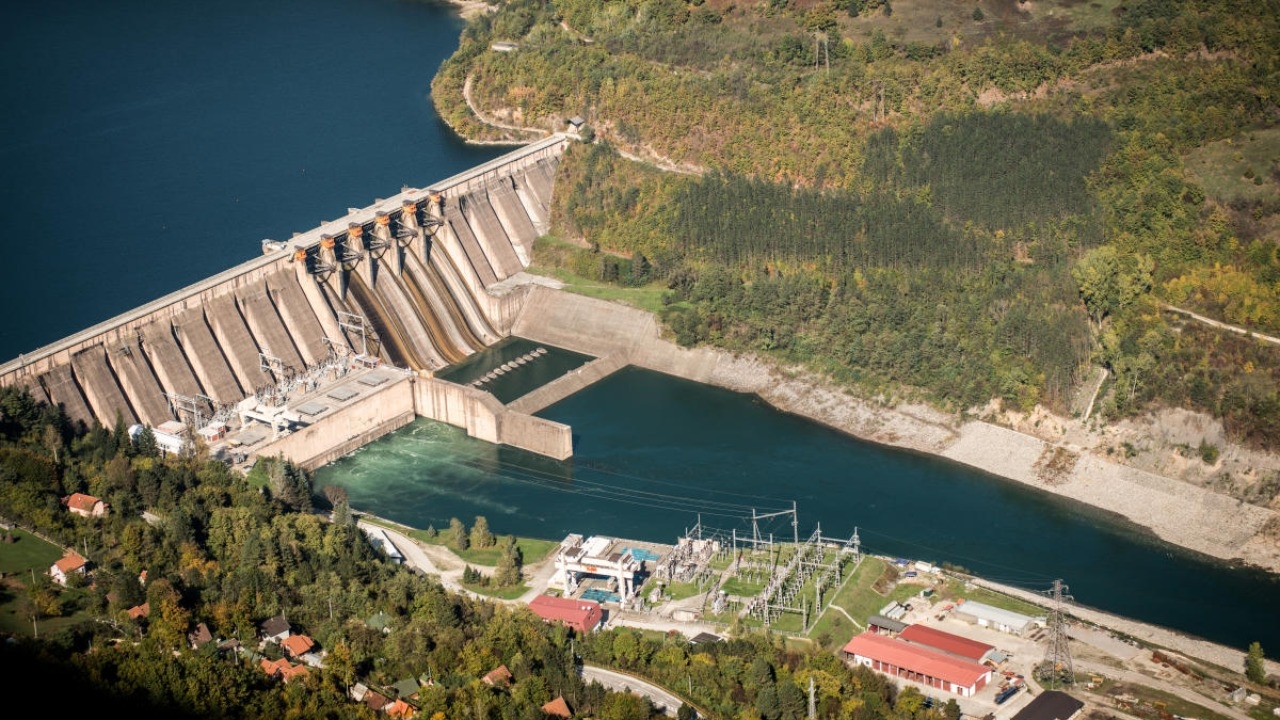

Hydropower Investments in Arunachal Pradesh
Accelerating the Construction of 12 Hydropower Stations with $1 Billion Investment
The Indian government is making a significant push to enhance the energy infrastructure in Arunachal Pradesh, with a focus on the hydropower sector. The government has committed approximately $1 billion for the construction of 12 new hydropower stations across the state. These projects aim to tap into Arunachal Pradesh's vast hydropower potential and transform the region into a powerhouse for renewable energy production, while addressing the increasing demand for clean and sustainable energy.
Key Aspects of the Hydropower Investment Initiative:
-
Capital Investment of $1 Billion:
-
The Indian government has allocated a substantial investment of $1 billion for the development of these hydropower projects.
-
This funding will cover construction, technical infrastructure, and sustainable development initiatives tied to the hydropower stations.
-
-
Construction of 12 Hydropower Stations:
-
The construction of 12 hydropower stations is set to significantly enhance the state's energy output.
-
These stations will harness the power of Arunachal Pradesh’s numerous rivers and high-altitude water resources, generating clean, renewable electricity.
-
The hydropower plants will vary in capacity, ranging from small-scale plants to large dams, making them adaptable to the state’s diverse geographical features.
-
-
Strategic Importance for Renewable Energy:
-
Arunachal Pradesh, often referred to as the “hydropower capital” of India, has enormous hydropower potential, with its many fast-flowing rivers and mountainous terrain.
-
By focusing on hydropower, the state is aligning itself with India’s renewable energy goals, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and contributing significantly to the national energy mix.
-
The state's hydropower development also supports India’s broader climate goals and carbon neutrality targets by promoting clean energy and reducing carbon emissions.
-
-
Energy Security and Supply Reliability:
-
The investment in hydropower will help address the growing energy demand in Arunachal Pradesh and neighboring states.
-
The hydropower plants will ensure energy reliability and stability, particularly in remote regions, where conventional electricity infrastructure has been lacking or inconsistent.
-
The projects are designed to cater to both domestic consumption and export power to neighboring states, potentially turning Arunachal Pradesh into an energy exporter.
-
-
Economic Growth and Employment:
-
The hydropower sector is expected to create numerous job opportunities during the construction phase and in the long-term for operation and maintenance of the power plants.
-
Infrastructure development related to these projects will also boost local economies, providing employment opportunities in construction, engineering, and ancillary industries.
-
-
Environmental and Social Benefits:
-
Hydropower is a clean, renewable source of energy that does not emit greenhouse gases, making it one of the most environmentally friendly energy options.
-
However, to ensure sustainable development, the Indian government will focus on environmental protection, socioeconomic development, and the welfare of local communities living near hydropower plants.
-
The government has emphasized environmental impact assessments and community consultations as part of the project planning and implementation.
-
Expected Outcomes:
-
Enhanced energy capacity in Arunachal Pradesh and other northeastern states.
-
Improved energy security, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
-
Significant contribution to India’s renewable energy targets, reducing reliance on non-renewable power sources.
-
Creation of sustainable livelihoods and economic opportunities for the local population.
-
Strengthened regional integration through cross-border energy trade with neighboring states.
With an investment of $1 billion and the construction of 12 hydropower stations, Arunachal Pradesh is poised to become a leading producer of renewable energy in India. These projects will not only boost the state's energy infrastructure but also help meet the country’s ambitious sustainability and climate goals while promoting economic development and creating job opportunities for local communities.
- Lakshadweep
- Delhi
- Puducherry
- PROPIINN
- Arunchal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chhattisgarh
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Tripura
- Telangana | Andhra pradesh
- Pulse
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- West Bengal
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Chandigarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Ladakh